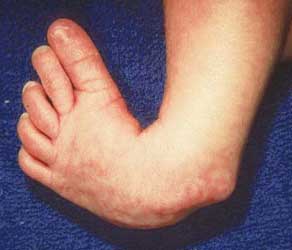
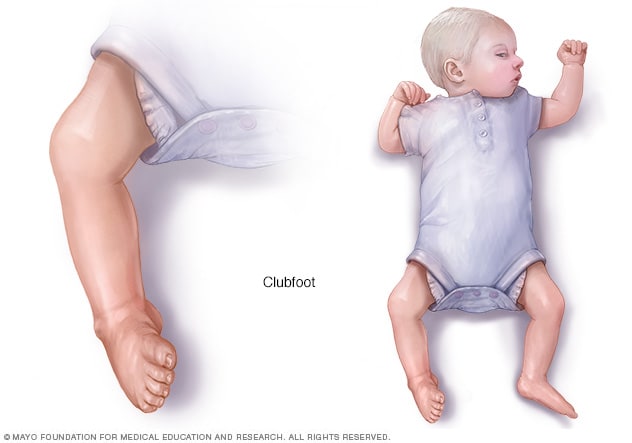
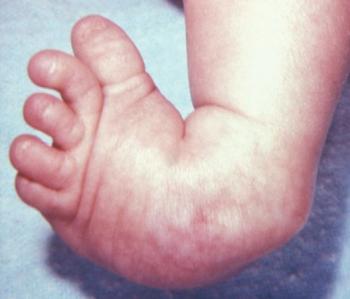
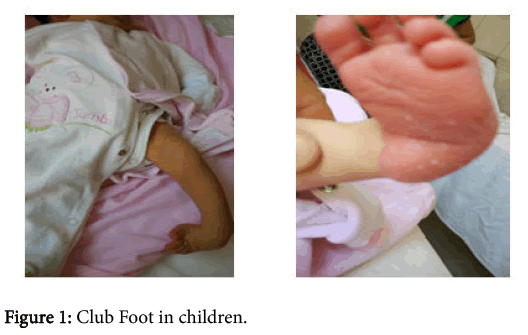
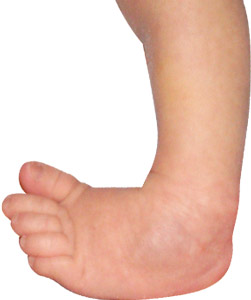
Clubfoot is a congenital deformity where the foot is rigidly turned inward and downward, and is misshapen like a club It can range from mild and flexible to severe and rigid, and can affect one or both feet In some cases, the calf muscle and affected foot may be slightly smaller than normal Occurring in about 1 in 1,000 babies, clubfoot isThe initial treatment of clubfoot is nonsurgical, regardless of how severe the clubfoot deformity is Treatment for club foot usually starts within a week or two of your baby being born The Ponseti method – Stretching and casting An examination of the feet is an essential component of an evaluation of a newborn A thorough examination can be performed quickly Despite its small size, the newborn foot is a complex structure

Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
Club foot deformity treatment
Club foot deformity treatment- Anterior Tibialis Transfer for Residual Clubfoot Deformity Kenneth J Noonan DEFINITION The incidence of residual deformity in congenital clubfoot ranges from 266% to 50%, regardless of the initial treatment provided2 The disparity in the reported incidence is due to varying severity of clubfoot deformity, different methods of treatment, and, in part, differingClubfoot occurs in 1 out of 1000 births Ideally, treatment of clubfoot should begin around a week after birth That's when the bones, ligaments and tendons are still soft and can be easily moved into the correct position However, treatment doesn't happen for all babies Sometimes clubfoot goes untreated during childhood and even adulthood
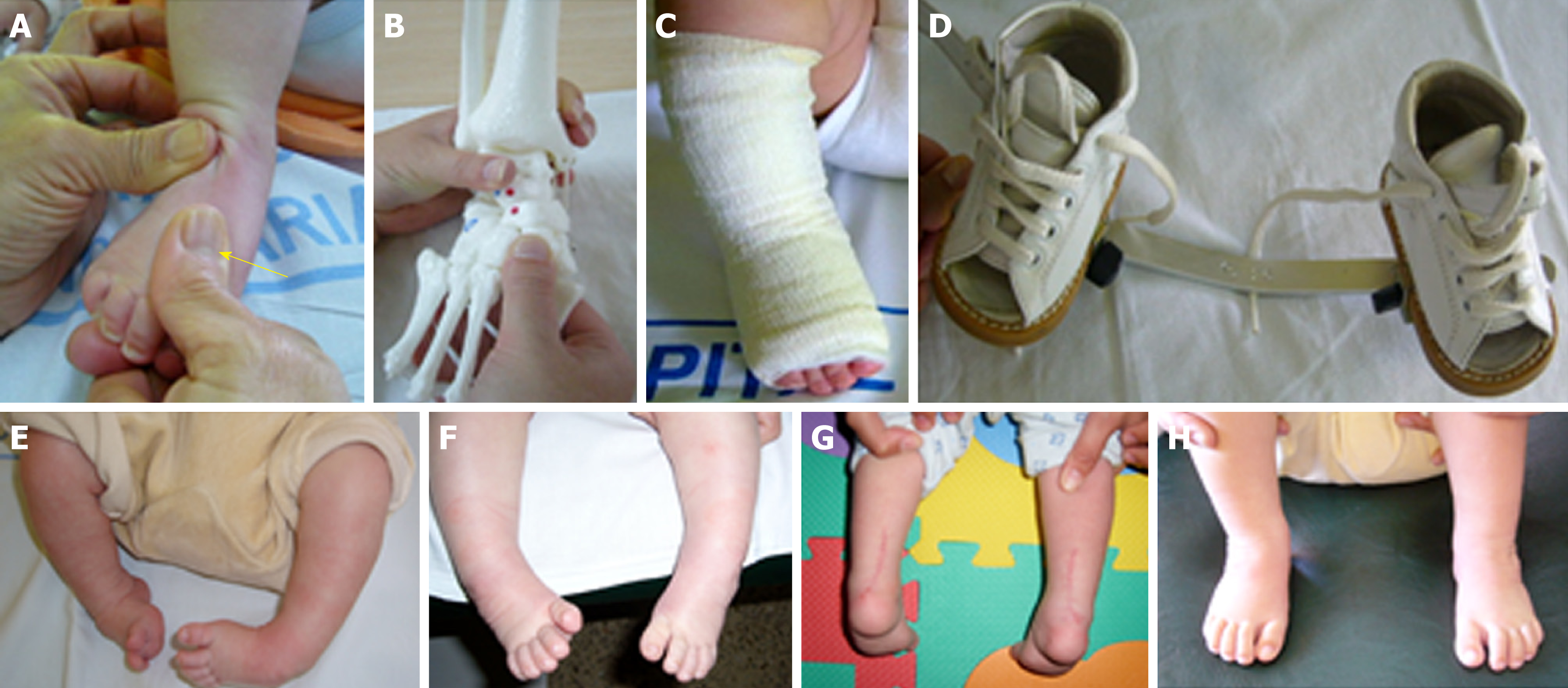



Functional Physiotherapy Method Results For The Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfoot
First Recurrence The deformity recurred in fiftythree feet (56 per cent) (Table 1) at ages ranging from ten months to five years, with an average of two and onehalf yearsSome authors stated that recurrences only occur when the clubfoot deformity is not completely corrected at the initial treatmentHowever, when we reviewed the roentgenograms made at the end of the primary treatment The treatment is of two approach;Clubfoot Clubfoot is a congenital condition, one that a baby is born with in which the foot or feet turn inward It won't go away on its own, but with early treatment, children experience good results Clubfoot treatment includes the Ponseti method, a nonsurgical treatment to move the foot to the right position Appointments & Access
121 Infants with clubfoot deformity are no longer subjected to major surgery, as the internet has helped to spread the word about a noninvasive method of manipulation and casting The Ponseti methodClub foot (also called talipes) is where a baby is born with a foot or feet that turn in and under Early treatment should correct it In club foot, 1 foot or both feet point down and inwards with the sole of the foot facing backwards Credit Club foot happens because the Achilles tendon (the large tendon at the back of the ankle) is too short Treatment Clubfoot refers to a condition in which a newborn's foot or feet appear to be rotated internally at the ankle The foot points down
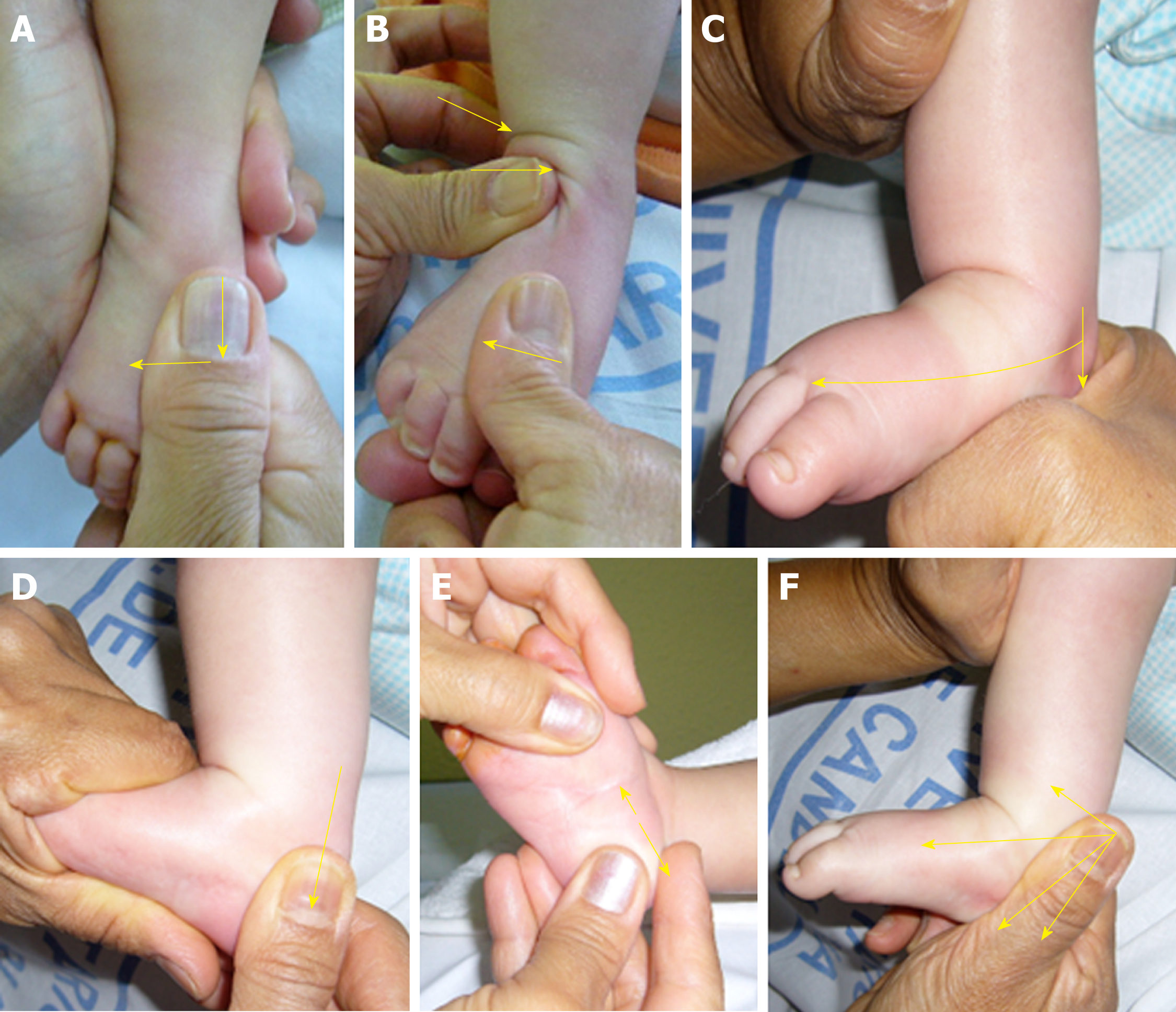
The most recognizable congenital foot deformity is the clubfoot deformity, which is characterized by plantar flexion of the ankle, inversion of the foot, and adduction of the forefoot Manipulative treatment of congenital foot deformities, which requires manual repositioning and serial casting, should be initiated immediately after birthClub foot refers to a tendon flaw that causes the hoof to be very upright Often, club foot affects both front legs with one being more severe than the other Club foot can occur before or after birth in foals After birth foals acquire club feet when the bones grow faster than the tendons Treatment varies with the age of the horse and Treatment of recurrent clubfoot deformity (cont) • rocker bottom deformity this is due to aggressive dorsiflexion of the foot against a hindfoot contracture Clubfoot is a deformity in which an infant's foot is turned inward, often so severely that with proper treatment, however, the majority of children are able to enjoy a wide range of physical activities with



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os
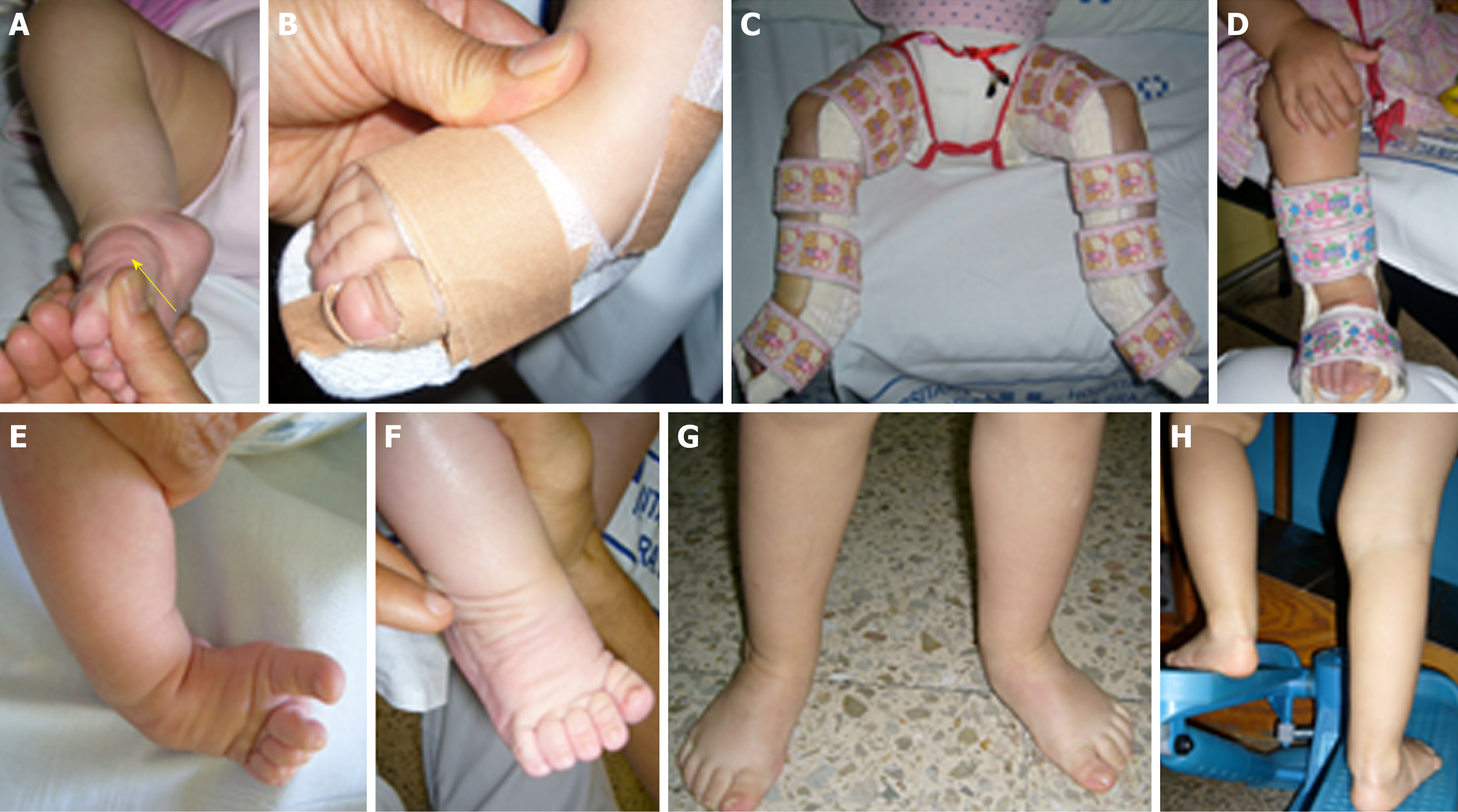



Functional Physiotherapy Method Results For The Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfoot
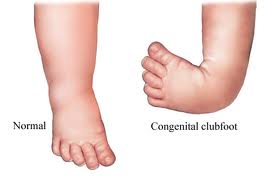
Clubfoot is a birth defect where one or both feet are rotated inward and downward The affected foot and leg may be smaller than the other Approximately 50% of cases of clubfoot affect both feet Most of the time, it is not associated with other problems Without treatment, the foot remains deformed, and people walk on the sides of their feetAll these factors contribute to the neglect of the treatment of clubfoot 50 % of children born with clubfoot do not have access to treatment / do not continue the treatment CTEV deformity and or with skin problem Courtesy 1 https Clubfoot resembles the head of a golf club, which is how it got its name Clubfoot is a congenital deformity, which means you're born with the condition Doctors usually diagnose it




Conditions And Treatments
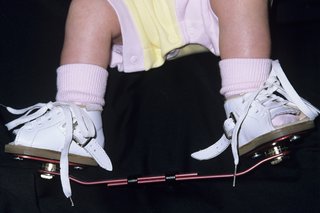



Club Foot Nhs
Clubfoot is a deformity in which an infant's foot is turned inward, often so severely that the bottom of the foot faces sideways or even upward Most cases of clubfoot can be successfully treated with nonsurgical methods that include stretching, casting, and bracingBackground Clubfoot is painless in a baby, but it can eventually cause discomfort and become a noticeable disability if left untreated These symptoms become more obvious and more of a problem as the child grows Objective This study was conducted to assess pattern of clubfoot deformity and adherence to ponseti treatment among children with clubfoot deformityThe initial treatment of clubfoot is nonsurgical, regardless of how severe the deformity is Ponseti method The most widely used technique in North America and throughout the world is the Ponseti method, which uses gentle stretching and casting to gradually correct the deformity
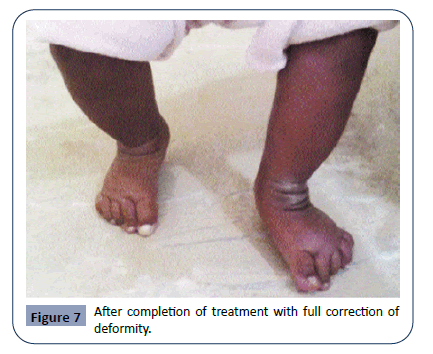



Cross Sectional Study Of Clinical Profile And Treatment Of Clubfoot By Ponseti Method Among Infants At A Tertiary Care Hospital Insight Medical Publishing




Correction Of The Neglected Clubfoot In The Adolescent And Adult Patient Foot And Ankle Clinics
Abstract Treatment of the congenital clubfoot (CCF) starts its development in the early th century and is still continuing today deformity gave grounds theHow is clubfoot treated without surgery?13yearold Chanda was abandoned by her family because she had clubfoot deformity due which she was leading a very tough life until she went through a clubfo



Club Foot Treatment Foot Disorders Foot And Ankle Specialist India




Treatment Of Relapsed Residual And Neglected Clubfoot Adjunctive Surgery Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics
Conservative and surgical approaches Regardless of the approach used, the treatment is aimed at correcting the deformity thereby preventing longterm disabilities rendering it fully functional and painfree Club foot can be treated in a combination of methods which includes; Club Foot Deformity Treatment Sometimes club foot can come back, especially if treatment isn't followed exactly The deformity in idiopathic club foot is both cosmetic and functional with associated hypoplasia of skin, muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments and neurovascular bundle on the medial side and the affected foot is smaller than the normal foot 27407 Foot Deformity Treatment Developed Date Source Washington University School of Medicine Summary Children born with a foot deformity that causes them to have a rigid flatfoot once



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
It is a congenital deformity that may affect both feet or only one foot And, with proper treatment, a significant majority of clubfoot patients enjoy 100 percent recovery Successful treatment enables them to walk normally and even participate in athletics Please note that, although the condition looks painful,The initial clubfoot treatment is nonsurgical as it depends on the severity of the foot deformity For clubfoot Ponseti method Is one of the most commonly used technique throughout the world which uses gentle stretching and casting to gradually correct the deformity Treatment should ideally begin shortly after birth, but older babies have also been treated successfully with thisGentle means in any club foot Thus, 15 out of 17 pa tients had a resistant club foot In Groups A, B and C, a relapse was defined as a club foot with a recurrent deformity needing treatment after the initial period of treatment in plaster was over (Laaveg & Ponseti 1980) Primary treatment in




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets




Functional Physiotherapy Method Results For The Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfoot
This study reviews the outcomes of treatment in our practice using the quantitative clubfoot assessment of the deformity (QCAD) Methods Thirty patients (38 cases of clubfoot) with congenital idiopathic clubfoot treated at Sarawak General Hospital were followedup for a2210 Clubfoot is a common congenital deformity that affects one in 1000 live births in the United Kingdom Most cases are idiopathic and not associated with other conditions Babies should be referred early for treatment Current best treatment is by casting and bracing according to the Ponseti method Results are better with manipulative methodsAnd treatment The deformity in idiopathic club foot is both cosmetic and functional with associated hypoplasia of skin, muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments and neurovascular bundle on the medial side and the affected foot is smaller than the normal foot 2 Current treatment of clubfoot deformity includes initial trials of




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital
/GettyImages-531856195-56c202e25f9b5829f867c91e.jpg)



Learn About Clubfoot Deformity In Newborns
Clubfoot occurs because the connecting structures between the leg and foot are short and too tight causing the foot to twist inward It is unknown what causes clubfoot However, there is an increased risk in families with a history of clubfeet Doctors at Riley at IU Health use a threestep process to treat clubfoot casting, tenotomy and bracingClubfoot is a foot deformity in newborns where the foot is rotated inwards (varus) and downwards (equinus) The vast majority of clubfoot deformities are congenital in nature, and therefore acquired during development in the uterus and not through heredity4 3 Goal and result of the Ponseti treatment The goal is to reduce if not eliminate all elements of the Clubfoot deformity to obtain a functional, flexible, pain free, strong, normal looking, plantigrade and normal shoeable foot




Clubfoot Deformities What Causes It And How Doctors Treat It Bones And Joints Oladoc Com




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
He coined the word 'orthopaedia' and laid down the principles of preventing and correcting deformities and he detailed the conservative management of clubfoot The treatment of the deformity came into the hands of bone setters and instrument makers and it was almost beneath the dignity of a surgeon to treat itClub foot deformity can usually be identified on prenatal ultrasound exam Some subtle cases may be missed on ultrasound but are easily diagnosed after birth Once the condition has been detected, a targeted ultrasound will be performed to rule out the presence of associated anomaliesWith majority of deformities like clubfoot, DDH etc can be identified, but after birth parents should consult with Child Ortho Care before going further with radical treatment Info@clubfoottreatmentcom



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine



Functional Physiotherapy Method Results For The Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfoot
Sometimes club foot can come back, especially if treatment isn't followed exactly With regard to congenital disorders, like a club foot or fused toes, these are typically foot deformity treatments and relief The affected foot and leg may be smaller in size compared to the other Current treatment of clubfoot deformity includes initial trialsRecurrent Clubfoot this is a clubfoot which has achieved a good result with Ponseti treatment, but the deformity has recurred The commonest reason is due to abandoning the braces early Neglected Clubfoot the neglected clubfoot is a clubfoot in a child older than 2 years, where little or no treatment has been performedThe orthopaedic literature on clubfoot deformity focuses on early intervention in a resourcerich environment, with numerous surgical options outlined for both primary treatment and treatment of the relapsed clubfoot7,9 There is very little literature available on treatment of the neglected clubfoot with major texts provid




Club Foot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus About Club Foot Patient
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-976611000-781e705fad0e43aca41e5f5fc82f7b7e.jpg)



Learn About Clubfoot Deformity In Newborns
Docker CE, Lewthwaite S, Kiely NT Ponseti treatment in the management of clubfoot deformity a continuing role for paediatric orthopaedic services in secondary care centres Ann R Coll Surg Engl 07 Jul (5)5102 Ippolito E, Ponseti IV Congenital club foot in the human fetus A histological study




Predicting Recurrence After Clubfoot Treatment Lower Extremity Review Magazine



Clubfoot Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic



How A Revolutionary Cure Put Clubfoot On The Global Health Agenda The Seattle Globalist




Clubfoot In Children Lurie Children S



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Merck Manuals Consumer Version




Clubfoot Foot And Ankle Deformities Principles And Management Of Pediatric Foot And Ankle Deformities And Malformations 1 Ed
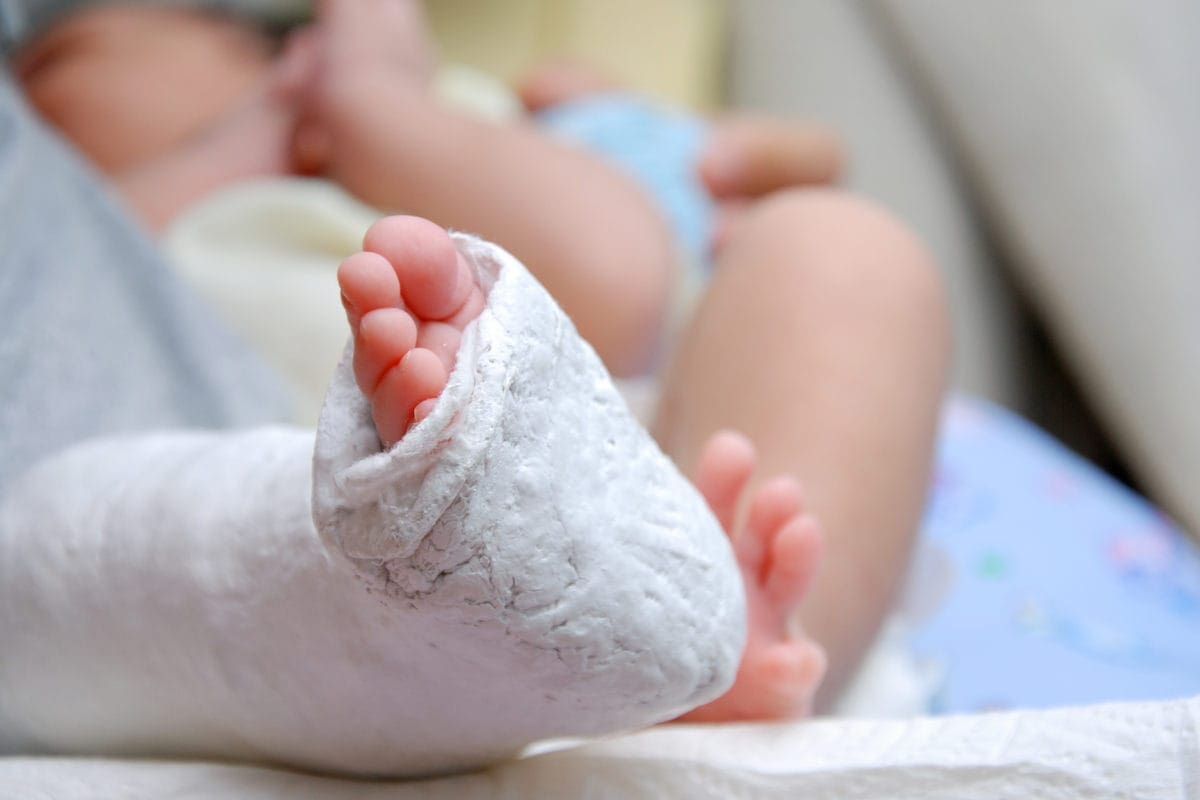




What Is Clubfoot Symptoms And Treatment Familydoctor Org




Clubfoot Repair Treatments Procedure Outlook



Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Ankle Foot And Orthotic Centre




Clubfoot Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis




Clubfoot Foot And Ankle Deformities Principles And Management Of Pediatric Foot And Ankle Deformities And Malformations 1 Ed




To Parents Of Children Born With Clubfeet University Of Iowa Stead Family Children S Hospital



Ultrasound




Clubfoot



Clubfoot Symptoms Stages Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis



Clubfoot Since Ancient Time Up To Now Omics International




Clubfoot Causes And Treatments Palos Hills And Mokena



Club Foot Herndon Congenital Deformity Treatment Vienna Va



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os




Fig 2 Radical Reduction In The Rate Of Extensive Corrective Surgery For Clubfoot Using The Ponseti Method American Academy Of Pediatrics
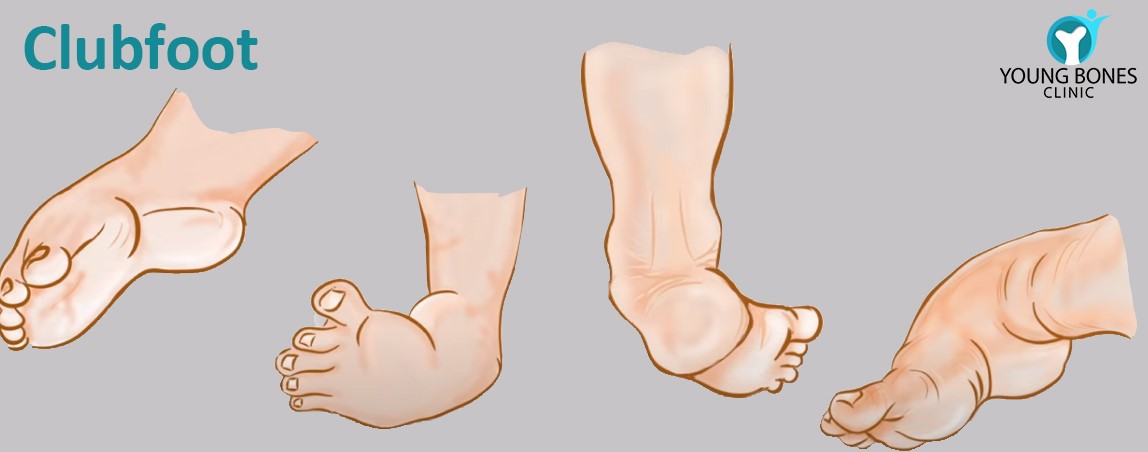



Clubfoot Treatment In Gurgaon Delhi Young Bones Clinic
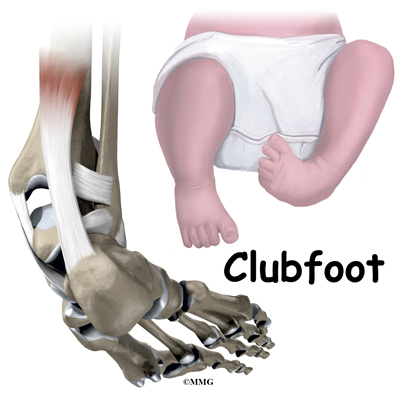



Clubfoot Eorthopod Com
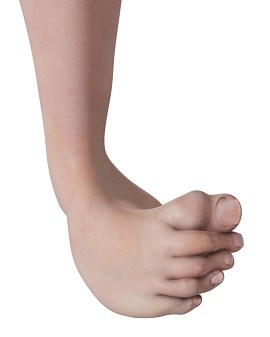



Congenital Deformity Treatment New York Ny Congenital Clubfoot New York Ny




Clubfoot Wikipedia
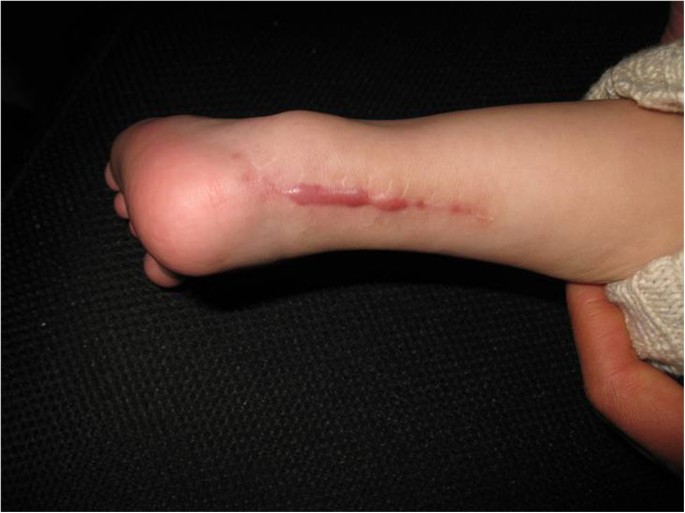



Manipulation And Brace Fixing For The Treatment Of Congenital Clubfoot In Newborns And Infants Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders Full Text




To Parents Of Children Born With Clubfeet University Of Iowa Stead Family Children S Hospital




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets




Demonstration Of Deformities Present In Clubfoot Download Scientific Diagram
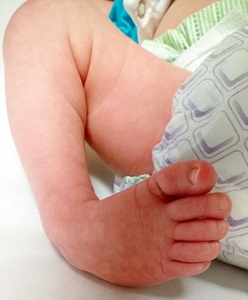



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets




Pdf Midterm Results Of The Ponseti Method In The Treatment Of Congenital Clubfoot Semantic Scholar




Treatment Of Relapsed Residual And Neglected Clubfoot Adjunctive Surgery Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics



Clubfoot Foot Deformity Club Foot Treatment Clubfoot Foot Surgery




Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram




New Tool To Assess Clubfoot Treatment Lower Extremity Review Magazine




A Fully Relapsed Of Clubfoot Deformity Following Incomplete Treatment Download Scientific Diagram




The 17 Abjs Nicolas Andry Award Advancing Personalized Medicine For Clubfoot Through Translational Research Springerlink




Ppt Treatment Of Clubfoot Deformities Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os



1




The Adult Sequelae Of Treated Congenital Clubfoot Foot And Ankle Clinics
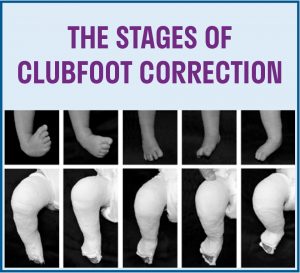



Treatment Strategies Paley Orthopedic Spine Institute
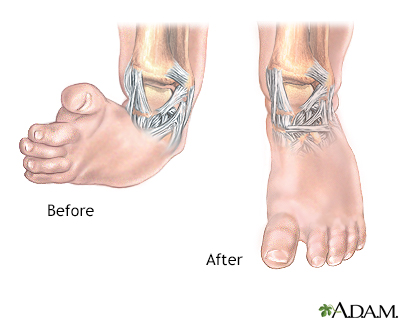



Clubfoot Information Mount Sinai New York
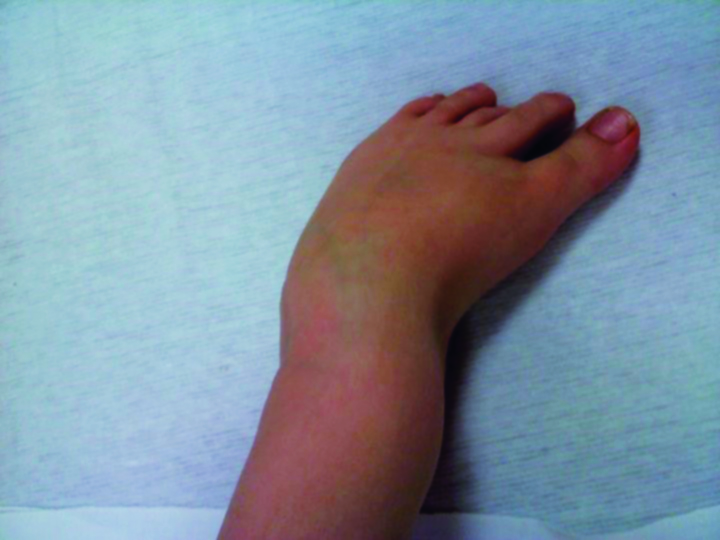



Clubfoot Deformities Get A Full Range Of Understanding pc Knowledge Center




Clubfoot Solutions Learn About Our Efforts To Treat Clubfoot




Pdf Selective Soft Tissue Release For Recurrent Or Residual Deformity After Conservative Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfoot Semantic Scholar




A F A A 7 Month Old Girl Presented With Unilateral Clubfoot With Download Scientific Diagram




Clubfoot Footcaremd



Neglected Idiopathic Clubfoot Successfully Treated By The Ponseti Method A Case Report Of An Adult Patient Who Started Treatment At 26 Years Of Age Journal Of Orthopaedic Case Reports



About Clubfoot



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os
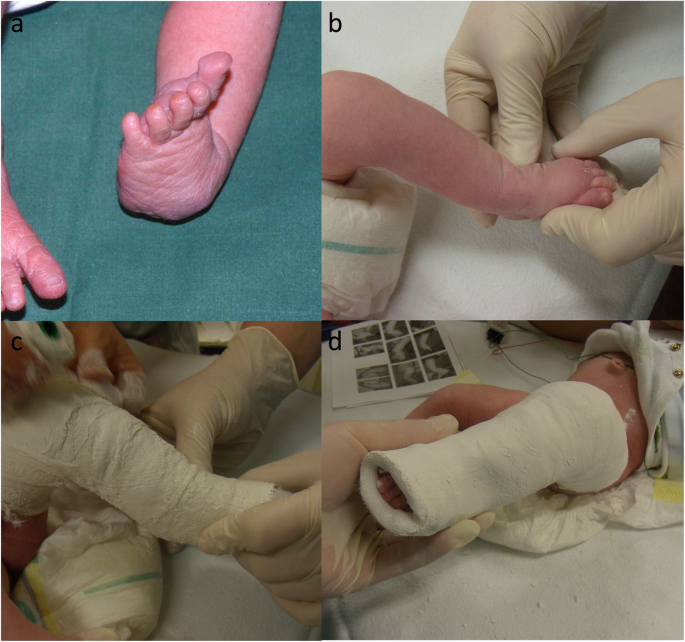



Clubfoot Treatment With Ponseti Method Parental Distress During Plaster Casting Journal Of Orthopaedic Surgery And Research Full Text
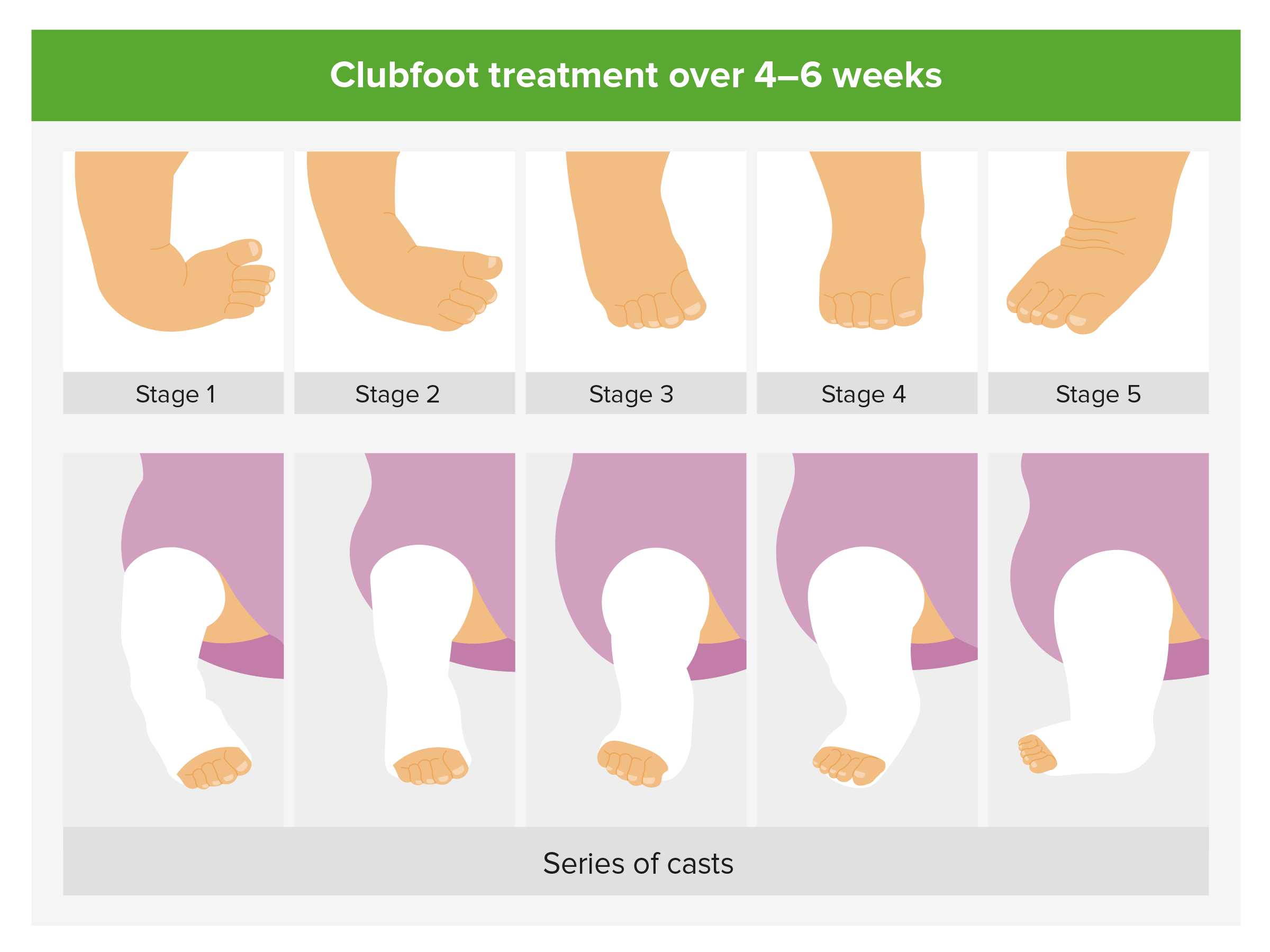



Foot Deformities Concise Medical Knowledge




Predicting Recurrence After Clubfoot Treatment Lower Extremity Review Magazine



Club Foot



1



Childrens Podiatry What Is Clubfoot
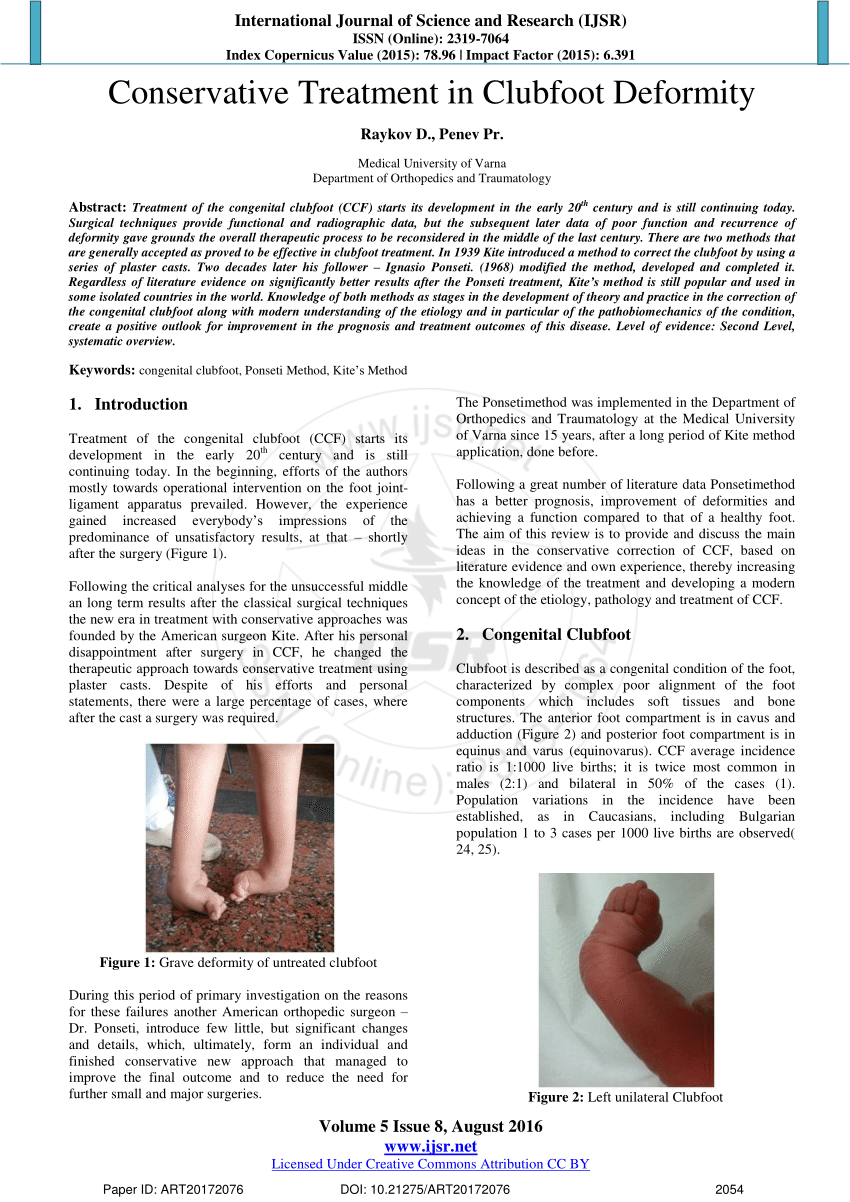



Pdf Conservative Treatment In Clubfoot Deformity



Changing Steps One Clubfoot At A Time Our Blog




Treatment Of Neglected And Relapsed Clubfoot With Midfoot Osteotomy A Retrospective Study




Clubfoot Deformities Pediatric Orthopaedics Navicent Health Macon Georgia Atrium Health Navicent




Clubfoot Children S Orthopaedic And Scoliosis Surgery Associates Llp



India S First Brace Bank Encourages People To Donate Used Clubfoot Braces Thehealthsite Com




Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Merck Manuals Consumer Version
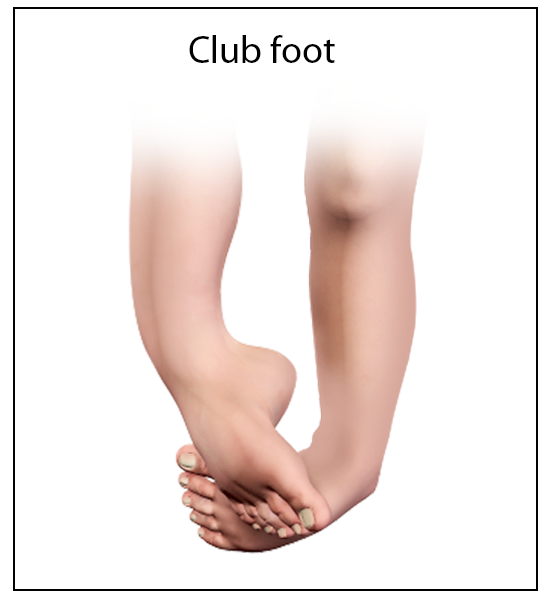



Club Foot Congenital Deformity Memphis Foot Deformity Memphis




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os
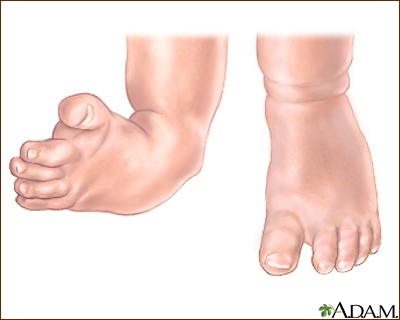



Antidepressants And Clubfoot Birth Defect




Idiopathic Congenital Clubfoot Initial Treatment Sciencedirect



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




Clubfoot Www Lowerextremity Com




To Parents Of Children Born With Clubfeet University Of Iowa Stead Family Children S Hospital
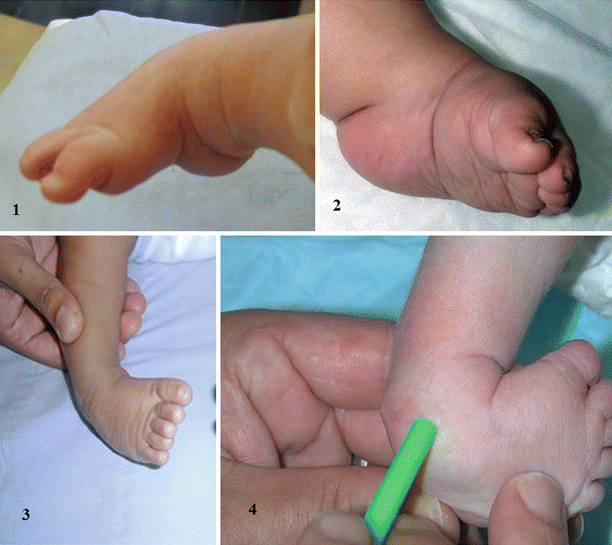



Evidence Based Treatment For Clubfoot Springerlink




Clubfoot Wikipedia



Club Foot Chicago Foot Care Clinic



1




Clubfoot Www Lowerextremity Com




Positional Clubfoot
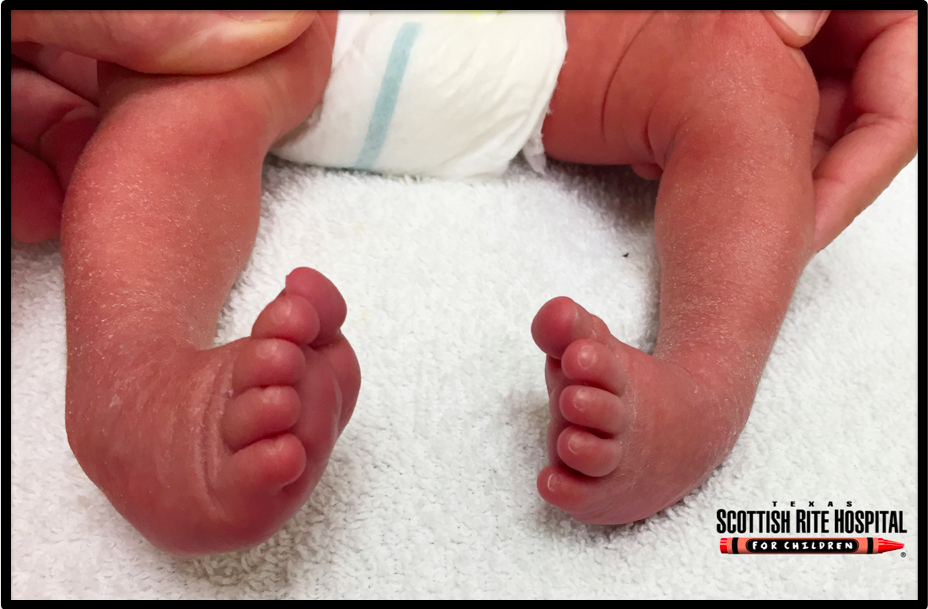



Clubfoot Deformity Footeducation




Congenital Idiopathic Talipes Equinovarus American Academy Of Pediatrics
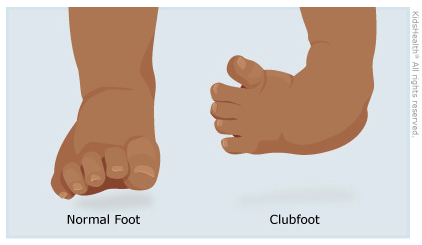



World Clubfoot Day June 3 The Rees Jones Foundation




Club Foot Talipes In Babies Causes Signs Treatment Youtube
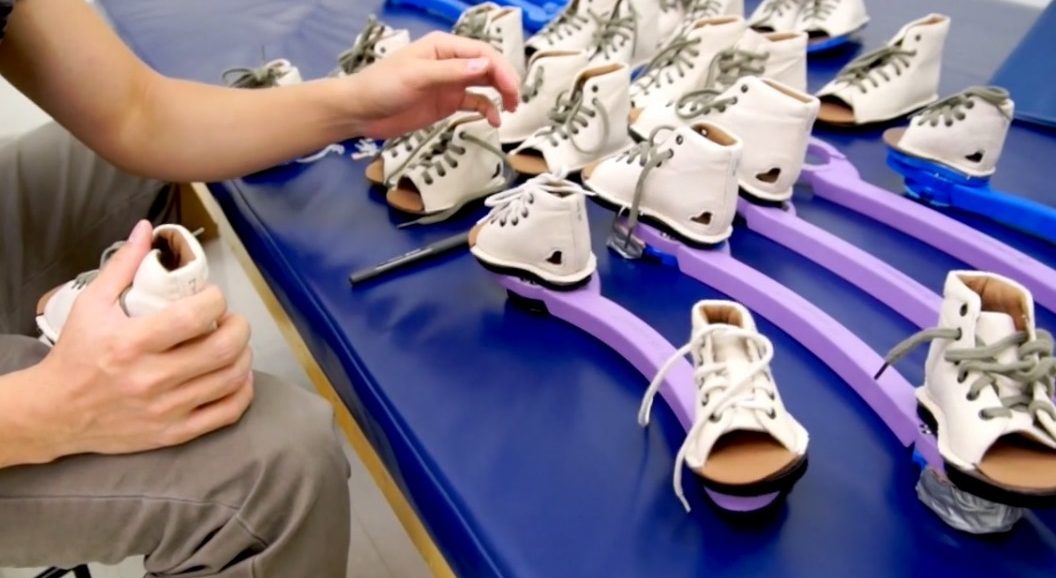




Sometimes Aid Is Transformative A Look At A Simple Affordable Clubfoot Treatment Scope



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿